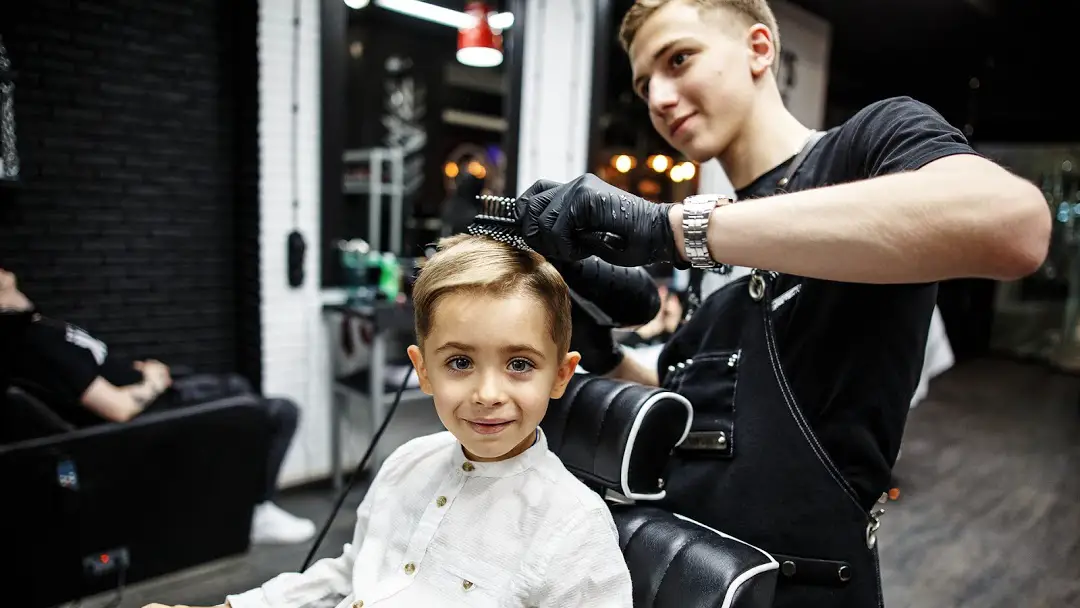
Barbers and Hairdressers in Eurasia
In Russian, there is no distinction between the words for “barber” and “stylist;” the word “парикмахер” in Russian refers a person who cuts hair for both men and women. A person visits a парикмахерская (barbershop; where the парикмахер works) to подстричься (have his/her hair cut). Not everyone goes to a парикмахер, of course, as some people стригут себя (cut their own hair).
Costs will differ greatly based on your location and what type of парикмахер you are seeking. Some высококлассные (high-end) парикмахеры can charge considerable sums. Increasingly popular are shops specializing in мужская стрижка (men’s haircuts), which also have услуги по уходу за бородой (beard services). These will often be more expensive options.
Some парикмахерские эконом-класса (economy class barbershops) can подстричь (provide a haircut) for prices that you probably shock you for being so low, especially if you just looking for something very simple like a military-style buzz cut.
Types of Hair and Styles
There are many ways to describe hair: длинные волосы (long hair), короткие волосы (short hair), волосы до плеч (shoulder-length hair), кудрявые волосы (curly hair), прямые волосы (straight hair), вьющиеся волосы (wavy hair), лысый (bald), and лысеющий (balding). Мужчины, старающиеся прикрыть лысину (men trying to hide bald spot) may try a зачёс (comb-over).
There are many different basic hairstyles, such as: for men – короткая стрижка (buzz cut), стрижка под горшок (bowl cut), стрижка ёжик (crew cut), ирокез (mohawk; note that they call it an “iriqoui” in Russian), а-ля Битлз (mod-top), маллет (mullet), and стрижка-шапочка (shag); for women – гарсон/под мальчика (crop), каре (bob cut), стрижка перьями (feathered cut), стрижка боб (pixie cut), гаврош (razor cut), and стрижка под стрижкой (undercut).
For men, there are several ways to fashion facial hair. Men can подравнивать/ побрить бороду (have their beard trimmed/shaved), постричь усы (style a mustache), or have бачки (sideburns).
There are also practical terms to describe specific actions that a парикмахер might take. For example, it is possible to simply подравнивать волосы (to trim hair), i.e. to убрать немного по краям (cut off a little bit at the ends). The парикмахер might ask, especially to men, if the hair should закрывать уши (cover the ears). Some people prefer their hair собраны сзади (blocked in the back) while others prefer распущены сзади (feathered in the back). Some people like their hair все одной длины (all one length) while others prefer слоями (layers). Some wear чёлка (bangs) and others don’t.
Besides different types of стрижки (haircuts) there are also many types of причёски (hairstyles): конский хвост (ponytail); бабетта (bun); коса (braid); косичка (smaller braid, often used for little girls); and французская коса (French braid). In many Slavic counties, a traditional hairstyle is to have a French braid go all the way around her head, in other words, заплетать косу вокруг головы (to braid one’s hair around one’s head).
Colors, Perms, and Products
Women will hold their hair in place with a variety of means including заколка (a barrette/hair clip/bobby pin), резинка для волос (elastic hair tie/scrunchy; sometimes referred to as a “резиночка” in conversational Russian), ободок (a hairband), лента для волос (hair ribbon), or, of course, лак для волос (hair spray), гель для волос (hair gel) or пенка/мусс для укладки волос (mousse).
In terms of hair color, a person can be блондин (a blond), брюнет (a brunette), с темными волосами (with black hair), or рыжий (a redhead). When красить волосы (dying hair), it is possible to красить волосы самому (color your hair yourself) or to красить волосы в парикмахерской (have your hair dyed by a stylist). Instead of dying all of their hair, some people get мелирование (highlights).
A person can also go to a парикмахерская in order to сделать химическую завивку (to get a perm; sometimes referred to as сделать «химию» in conversational Russian), сделать укладку / сделать прическу (set hair or arrange hair), or сделать наращивание волос (get hair extensions). Another option is to use a плойка (curling iron) or бигуди (hair curlers) at home. Some Russians делают прическу «гофре» или гофрируют волосы (crimp their hair), some делать пробор посередине или на боку (part their hair in the middle or on the side).
To keep your hair stylish, you’ll need some of these basic hair items: расческа (comb), щётка для волос (brush), предохранительная завязка для волос (hair tie for ponytails/braids), фен (hair dryer), and выпрямитель волос (hair straightener/flat iron).
Culture and Etiquette
Although the situation is changing, it is not customary in most locations оставить чаевые (to tip) the person who cuts your hair. Generally this will be appreciated, however, especially if you state directly what the money is for and that you are satisfied. If you would like to leave a tip, you might say “Это вам на чай. Спасибо вам большое” as you hand it to the person.
However, you should also know that the service industry in many Eurasian countries functions a bit differently. Culturally, there may be some significant differences to expect from a парикмахер, primarily in that you may not receive at all what you asked for. Obviously, some of this may come from linguistic difficulties in trying to convey what you want. Few парикмахерскы, no matter what they are charging or where they are operating, will speak fluent English. The terms above should help you. However, there seem to be many парикмахеры who really only know a few basic cuts and tend to give you whichever seems to most approximately match your current style. This tends to be more frequent among older парикмахеры charging lower rates. However, younger парикмахеры charging higher rates may consider themselves artists well versed in the science of hairstyles and thus provide you with what they believe would suit you best. Of course, again, much of this can be avoided if you clearly state your desires (in Russian if needed!) and keep an eye on the progress and provide commentary.
Many things are harder abroad, especially if you are operating in a language you are still learning. However, whatever happens, know that this is all a growing experience – and will make for great stories when you get back home!
You’ll Also Love

Russian MiniLessons: The Russian Bath House
The following bilingual Russian MiniLesson is meant to build your vocabulary by providing Russian phrases within English text. Hover over the bold Russian to reveal its English translation. has always played an important part in Russian culture. Since ancient times, Russians have said that . The баня was also thought in previous times to be highly […]

Medical Russian Vocabulary: Doctors and Folk Remedies
Healthcare abroad is often different from what we’ve experienced at home. How doctors and homestay facilitators may react to certain illnesses is different. Medicines and procedures that can be prescribed by doctors are often different. Over-the-counter brands that can be recommended by pharmacists are often different. Home remedies offered by friends or homestay facilitators can […]
Самый лучший разговорник – The Best Phrasebook Ever
The following list of phrases are meant as educational humor. Some are just silly, some are useful, some will be understood by all, and some only by those who have spent time in Russia. Some of these have been around online as jokes for some time – others were added based on common experiences that […]

Russian Vocabulary about Love and Relationships
Russian has many ways of expressing affection and describing the various phases of falling in love and establishing a relationship. This bilingual resource is meant to build your vocabulary by providing Russian phrases within English text. It covers everything from meeting to dating and marriage and in multiple styles from slang to classical literary prose. […]

Orthodox Easter: Its Language and Symbolism
Orthodox Easter is by far the most important religious holiday in most Slavic lands and is the busiest day at most Russian Orthodox churches across the globe. The holiday is steeped in history and mystic symbolism. The following is a dual-language article meant to teach you about history and culture of Orthodox Easter while allowing […]





