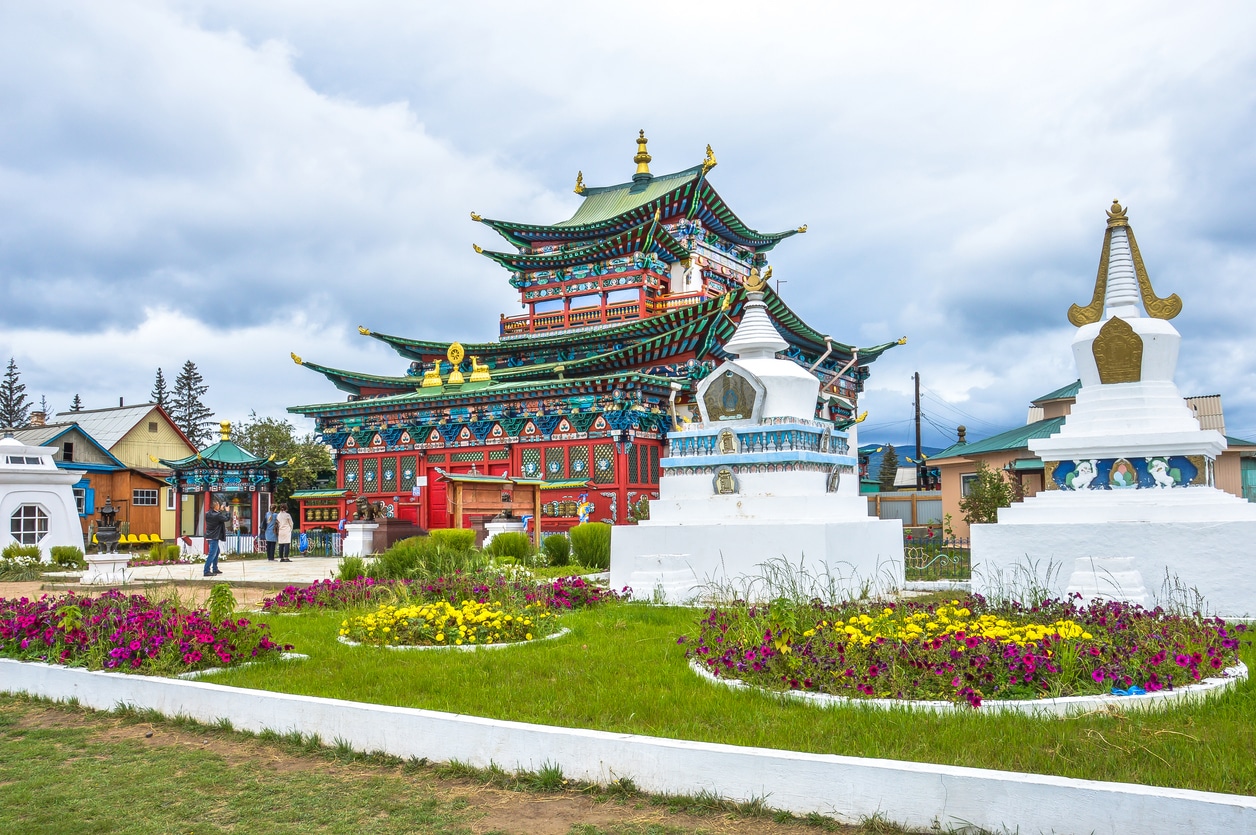
In this text, Tajik blogger Roxana Burkhanova describes, in Russian, the history and current status of Buddhism in Russia. Buddhism is a small but historically important minority faith in Russia, especially in the Southern regions of Tuva, Buryatia, and Kalmykia. The material below details both the challenges that Buddhists have faced in integrating to wider society and the remarkable revival that Buddhism has enjoyed in Russia.
This is part of a larger series of intermediate Russian lessons known as Моя Россия, in which Roxana explores minority populations in Russia as well as economic and demographic issues there. Моя Россия builds upon Olga’s Blog, another set of intermediate Russian lessons that give shorter texts that focus more on daily life and cultural issues. All of these lessons have been sponsored by SRAS, an organization that encourages the study of Eurasia from abroad through free resources and offers study abroad programs in Eurasia.
We will start with a brief synopsis in English before presenting the Russian text. As the Russian text was originally written in 2016, we have also provided a small update in English to the information presented there. All bold words and phrases have annotation below. Red words and phrases indicate the subject of this blog entry’s punctuation lesson. Asterisks indicate slang.
Buddhism and Buddhist Regions in Russia – Synopsis and Update in English
Buddhism in Russia has a long and complex history, tracing its roots to the early 17th century. In modern Russia, Buddhists are largely concentrated in provinces where they have historically been dominant. This includes Kalmykia, in the North Caucasus, as well as Tuva and Buryatia in East Siberia.

These regions are named for Mongol or Turkic cultures who had converted to Buddhism and whose lands were forcibly incorporated into the Russian empire. Russia at the time recognized Buddhism as an official religion, and, although its influence always remained small, its influence was allowed to spread.
Despite Soviet-era repression, Buddhism began to revive in Russia after World War II, with significant growth starting in the 1980s. Since the fall of the USSR, major Buddhist centers have been revived or constructed. For instance, The enormous new Golden Temple in Kalmykia and the old Ivolginsky Datsan in Eastern Siberia, symbolize this resurgence. Russia continues to support Buddhism as a “traditional religion” of Russia.
There are also communities and small Buddhist religious centers in major cities like Moscow and St. Petersburg, opened as many young people moved from these regions to these cites to seek greater educational and economic opportunities.
Russia’s historically Buddhist provinces are all relatively poor. Kalmykia is largely agricultural and has suffered from low birth rates and high emigration. Tuva has significant mining in addition to agriculture and has some of the highest birth rates in Russia. However, it is also a poor region suffering from high outmigration. Buryatia is best developed and diversified of the three with some forestry and tourism, but is also poor. These regions, and especially Tuva, have had high enlistment rates to the Russian military since the start of the war in Ukraine and correspondingly high casualty rates.
Overall, the total number of practicing Buddhists in Russia remains relatively significant but fairly small, with fewer than 500,000 active practitioners, or less than one half of one percent.
Религия в России – Буддизм
Мы уже успели поговорить о православии, язычестве и исламе. Теперь настало время поговорить о буддизме, который имеет долгую историю в России. В Российской империи он считался официально признанной религией. Буддизм появился в империи с начала XVII века, когда некоторые калмыцкие племена приняли российское подданство. В это же время Российская империя захватила территории, принадлежавшие сибирским ханам в Западной Сибири, монгольскому государству в Южной Сибири, а также местным племенам и китайскому императору в Восточной Сибири и на Дальнем Востоке. Некоторые из этих территорий были заселены буддистами. В XVII-XVIII веках некоторые народы России перешли от шаманизма к буддизму, особенно буряты, а позднее – тувинцы в Восточной Сибири.
Бурятия, Калмыкия и Тува – это три традиционно буддистских региона, большинство жителей которых являются буддистами.
Буддизм в Калмыкии: история и культура

В Калмыкии, например, в 2005 году был построен самый большой буддистский храм России и Европы. Кстати, познакомились с буддизмом впервые калмыки очень давно, еще в 8 веке. Тогда еще они называли себя ойратами (ойраты или современные калмыки – это группа западных монголов) и обращались в буддизм вместе с остальными монголами. В 14 веке, когда ойраты были включены в империю Чингисхана, они еще ближе познакомились с тибетским буддизмом, популярным в империи. В 17 веке ойраты стали заселять территорию между реками Дон и Волга и основали здесь Калмыцкое ханство, подчинявшееся российскому правительству. Тогда же буддизм распространился среди всех слоев калмыцкого населения, многие из которого практиковали шаманизм, и сыграл важную роль в складывании калмыцкого самосознания. В 18 веке большая часть калмыков отправились назад, в свои бывшие территории в Западной Монголии, теперь контролируемой Китайской империей. Это настолько ослабило Калмыцкое ханство, что оно было упразднено. Другой удар калмыки пережили в годы сталинского террора, когда они были депортированы в Среднюю Азию, Сибирь и Алтай в 1943 году. Уже в 1956 году им было разрешено вернуться обратно, но в процессе депортации минимум 1/3 часть депортированных калмыков погибла, а многие элементы культуры были утрачены. Сейчас в большинстве своем калмыки России проживают в Республике Калмыкия, говорят на калмыцком и русском языках и продолжают проповедовать буддизм.
Тувинский народ и симбиоз буддизма с шаманизмом
Тувинский народ – это этническая группа Южной Сибири. Тувинский язык сложился к 10 веку, а сам тувинский народ окончательно образовался к 13-14 векам. Тувинцы жили под властью как Монгольского государства, так и Китайской империи. Долгое время тувинцы проповедовали шаманизм, но в 13-14 веках тувинцы познакомились с тибетским буддизмом, который сросся с шаманизмом и образовал с ним симбиоз. Тувинская церковь не стала искоренять шаманизм, а проявила терпимость к нему. В 20 веке на какое-то время тувинцы образовали свою независимую республику, а в 1944 году присоединились к СССР. Сейчас они проживают в российской Республике Тува и говорят на тувинском и русском языках. Большинство из них – буддисты, однако немало тувинцев все еще проповедуют шаманизм. Кстати, Сергей Шойгу, министр обороны РФ и один из наиболее популярных российских политиков, – тувинец.
Бурятия и буддизм: становление народа

Буряты образовались из множества различных племен, не имевших общего названия, проживающих в районах Добайкалья и Забайкалья. Окончательно бурятский народ сложился к концу 18 века, когда в Забайкалье прибыли ойратские племена (те самые, которые образовали Калмыцкое ханство, переселившись к реке Волге из Монголии). Государство у бурят впервые появилась в годы Гражданской войны, называлось оно Бурят-Монголия. К 1923 году на его месте была образована Бурят-Монгольская АССР, которая сейчас называется Республика Бурятия. До принятия буддизма буряты были шаманистами, а в 16 веке, когда в Бурятию пришел тибетский буддизм, буряты сохранили большое количество шаманских верований. С признанием буддизма одной из основных религий России в 1741 году связано формирование образа жизни и самосознания бурятского народа.
Возрождение буддизма после советского времени и сейчас
В советское время велась жестокая борьба с буддизмом; частичное возрождение буддизма началось уже в 1945 году, после войны. Однако истинное возрождение религии началось лишь с 1980-х годов, когда стали открываться старые и строиться новые дацаны, буддистские монастыри-университеты. Для многих народов России буддизм стал символом национального и духовного возрождения.
Сейчас в России насчитывается несколько буддистских общин и организаций. У буддистов России нет централизованного органа, который объединял бы их всех. Буддизм популярен не только среди народов, традиционно проповедующих его, но и среди русских. Буддистские общины возникли в Москве, Санкт-Петербурге, Самаре и в других крупных городах России. Однако численность практикующих буддистов составляет не более 500 тысяч человек.
В следующей части мы обсудим иудаизм и анти-семитизм, их историю и современное положение иудаизма в России.
Vocabulary and Cultural Annotations
Буддизм – Buddhism
Калмыки – The Kalmyk people or Kalmyks are the Oirats in Russia, whose ancestors migrated from Western Mongolia (was also called Alliance of the Four Oirat tribes or Four Oirat or Oirads) in 1607. They created the Kalmyk Khanate in 1630–1724 in Russia’s Lower Volga region. Today they form a majority in the autonomous republic of Kalmykia on the western shore of the Caspian Sea.
Подданство – it’s the same as a citizenship (гражданство) but in Russian historiography подданство is only possible in states with monarchy. It means more of a connection between a person and a monarch, person and a crown. Гражданство has far more wide meaning.
Сибирское ханство – The Khanate of Sibir, also historically called the Khanate of Turan was a Turco-Mongol Khanate located in southwestern Siberia. The Sibir Khanate was itself once an integral part of the Mongol Empire, and later the White Horde and the Golden Horde. The Sibir Khanate was the northernmost Muslim state in recorded history. Its conquest by Yermak Timofeyevich in the end of the 16th century was the beginning of the Russian conquest of Siberia.
Сословия – estates of the realm, class
Республика Бурятия (Бурятия) – The Republic of Buryatia (Buryatia); its capital is the city of Ulan-Ude.
Республика Калмыкия (Калмыкия) – The Republic of Kalmykia (Kalmykia); it is the only region in Europe where Buddhism is practiced by the majority of the population. Its capital is the city of Elista.
Республика Тува (Тува) – The Tyva Republic (Tyva or Tuva). It lies in the geographical center of Asia, in southern Siberia. Its capital is the city of Kyzyl. From 1921 until 1944, Tuva constituted a sovereign, independent nation; however, it was recognized only by its neighbours: the Soviet Union and Mongolia. A majority of the people are Tyvans, but Russian is also spoken extensively.
Ойраты – Oirats are the westernmost group of the Mongols whose ancestral home is in the Altai region of western Mongolia. Although the Oirats originated in the western parts of Mongolia, the most prominent group today is located in Kalmykia, a federal subject of Russia, where they are called Kalmyks.
Чингисхан – Genghis Khan (1162 – 1227) was the founder and Great Khan (emperor) of the Mongol Empire, which became the largest contiguous empire in history after his death.
Калмыцкое ханство – The Kalmyk Khanate was an Oirat khanate on the Eurasian steppe; it was a part of Russia but for some time was free to lead it’s own foreign policy. It covered the area called Kalmykia and the surrounding areas stretching from Stavropol to Astrakhan. For over a hundred years the Kalmyk alternately raided the southern borderlands of Russia but also protected southern borders of Russia and engaging in many military expeditions against the Muslim tribes of Central Asia, the North Caucasus and Crimea.
Самосознание – in this case it’s synonymous to “самоопределение” or “самоидентификация”- self-identification as an ethnic, cultural, religious, national group.
Министр обороны РФ – Minister of Defense of the Russian Federation.
Гражданская война – in this case I talk about The Russian Civil War (November 1917-October 1922); a multi-party war in the former Russian Empire immediately after the Russian Revolutions of 1917, as many factions vied to determine Russia’s political future. The two largest combatant groups were the Red Army, fighting for the Bolshevik form of socialism, and the loosely allied forces known as the White Army, which included diverse interests favoring monarchism, capitalism and alternative forms of socialism, each with democratic and antidemocratic variants.
Punctuation Focus: Commas and Dashes
I. If an apposition is a proper noun, it is marked with commas if they are needed for clarification or give additional information to a defined noun (that is also a common noun!).
Ex.: Их дочь, Наташа, встретила нас.
Мои друзья, Петя и Алеша, помогли мне.
In speech pauses before and after apposition show that it clarifies a defined noun. Before such appositions you can put phrases «а зовут его», «а именно», «то есть» and it won’t change the meaning of the sentence.
II. Appositions marked with commas can be connected with a sentence with these words: «то есть», «или» (=то есть), «например», «по происхождению», «по имени», «по фамилии», «по прозвищу», «родом» and so on.
These words work like a part of an apposition and you have to put a comma before them and you can’t put one after them.
Ex.: Многие жители города, например_ студенты, участвовали в этой акции.
If an apposition is connected with a sentence with the conjunction «как» then it has to be marked by commas only if this conjuction «как» has the meaning of reason (=по причине).
Ex.: Как опытный турист, Петров был выбран старшим (=he was chosen as a leader because he was an experienced tourist).
If the conjuction «как» means «в качестве» then no commas needed.
Ex.: Его молчание было расценено_ как невежливость (his silence was seen as impoliteness)
III. Sometimes appositions can be marked with a dash if:
1. before an apposition you can add words «а именно», «то есть» and it won’t change the meaning of the sentence.
Ex.: Он очень любил эту игру – шахматы (а именно какую игру он любил?)
2. the independence of an extended apposition have to be marked in the sentence.
Ex.: Мы въехали в Ивантеевку – большое просторное село с ухоженными серебряными улицами.
3. an apposition clarifies a defined noun (in this case use dash from both sides).
Ex.: Ясень – теплолюбивая порода – страдает от весенних заморозков (ash-tree suffers because of the cold why? Because is a tree that likes warmth)
4. to clarify that it’s an apposition in the sentence where it’s not clear (when this apposition belongs to one similar member of a sentence in the sentence with a list).
Ex.: На террасе собрались хозяин дачи, его сын – мой приятель, соседи и их дети.
You’ll Also Love

Russian Vocabulary: Haunted Places in Russia
Russian folklore is rich with stories of spirits, haunted places, and supernatural forces that influence daily life. These beliefs shape how certain locations, from uncivilized wilderness to abandoned homes, are viewed in the collective imagination. Unclean spirits, or нечистая сила, are believed to settle in ominous spaces like crossroads, swamps, and even ordinary houses if […]

Quarantine Diaries: Русские мемы о коронавирусе
Quarantine Diaries is a series of free language lessons from SRAS. Each lesson can take a variety of forms but all focus on building intermediate and advanced vocabulary and listening skills. Read the text and familiarize yourself with the new vocabulary (you can hover over the bold Russian to reveal its English translation). Then, watch […]

Islam in Russia: Моя Россия Blog
In this text, Tajik blogger Roxana Burkhanova describes, in Russian, the history and current status of Muslims in Russia. Islam is the largest minority faith in Russia and Muslims are a growing and important demographic there, especially among immigrants from Central Asia. The material below details both the challenges that Muslims have faced in integrating […]

Russian MiniLesson: Funeral Lunches and Related Russian Vocabulary
The following was written by Caroline Barrow, a former SRAS Home and Abroad Scholar now working in Kazakhstan. Through an acquaintance there, she was invited to a traditional Russian funeral lunch – and shares her experience here. Each culture has its own way of honoring those who have left this world. Russians do this in […]

What is the First Day of University Like in Russia? Olga’s Blog
Below, Olga discusses what a first year freshman experiences on day one of their college education. The day offers no classes. It is instead filled with speeches, handshakes, and status symbols. All of this is highly indicative of the role of formality and ceremony in Russian education and Russian society. This resource is part of […]





